Job Costing In QuickBooks
QuickBooks is designed to help you plan, measure, and monitor company and job results. You can even use QuickBooks Job Costing Features to Achieve Your Gross Profit Goals!
Use its management reporting tools to immediately SEE operating and financial results. Proactively correct problems – before they spin out of control – so that you achieve your Gross Profit goals!
Or, after you take a deeper look, you may decide that you can modify your plans or gross profit goals…
QuickBooks Job Costing
QuickBooks comes with a set of tools that allows you to customize your QuickBooks accounting to simplify job costing, create job costing reports, properly invoice jobs, and improve the accuracy of your bids by properly estimating your job costs.
Before you get started delving into the details of QuickBooks Job Costing, it’s important to understand an overall model that significantly increases the power of your financial decision-making.
QuickBooks and the “pM3 Business Management Model”
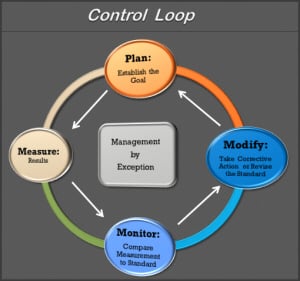
It’s called the “pM3 Business Management Model”:
 Plan: Establish specific, measurable quantity and/or financial goals. For instance, set up a plan to meet your Gross Profit targets.
Plan: Establish specific, measurable quantity and/or financial goals. For instance, set up a plan to meet your Gross Profit targets.
…- Measure: Record operating and financial results for jobs and company overhead costs.
… - Monitor: Compare your plan or standard to actual results.
- Based on what you see, you can begin to Manage by Exception. This means that you can focus your efforts on areas that are not lining up with the plan.
…
- Based on what you see, you can begin to Manage by Exception. This means that you can focus your efforts on areas that are not lining up with the plan.
- Modify: Confirm that your information is accurate, and do one of the following:
- Take corrective action (if possible).
- Find out why things didn’t work as planned. Then, you can establish a way to keep the issue from arising again in the future.
- Review your plans. If something was incorrect or overlooked, make sure the next plan or standard is more accurate.
If you’re not already following these four fundamental (and critical) business management action steps, it’s time to customize your QuickBooks accounting system to support this tried-and-true management model.
But Make These Setup Changes In QuickBooks Before You Begin Using These Four Powerful Management Tools…
Because you’ll want to use QuickBooks to take advantage of these critical four steps, you’ll first need to create logical, meaningful “Lists” within the software. As you create the Lists, you’ll want to keep gross profit reporting in mind.
QuickBooks Accounts – the Foundation of Your Accounting System
For Income Statement (Profit & Loss) reports, you’ll be able to establish accounts based on the following account types in QuickBooks:
- Income
- COGS aka Cost of Goods Sold (for direct and indirect production costs)
- Expenses (for company overhead)
- Other income and expense
Account-based reports create totals for each account type and provide step-based results in your report for Gross Profit, Net Ordinary Income, and Net Income (amounts and percentages). Thus, the lists you create become the basis for the reports you’ll use to Plan, Monitor, and ultimately control your gross profit outcomes.
QuickBooks Items – the Secret to Job Costing In QuickBooks
 Items are a powerful QuickBooks job costing and monitoring tool. If you need to see detailed and alternative views of job costs, you will definitely want to understand and use Items!
Items are a powerful QuickBooks job costing and monitoring tool. If you need to see detailed and alternative views of job costs, you will definitely want to understand and use Items!
Each QuickBooks Item links to one or more accounts (no double entry required for job costing). You can design your Item List to be able to access reports that show not only Actual results, but Estimated vs. Actual results for each job phase, in job-stage order, for direct labor, subcontractors, materials, and other costs.
Create Your Own Subtotals – In Accounts, Items, and Other Primary Lists
There are other important “structural” lists in QuickBooks that you will want to explore. Why? Because reports are based on lists – each list plays an important role in determining the quality of information that you’ll be able to obtain from your system.
QuickBooks Reporting Tip
Here’s a tip that can have a major impact on the quality of your reports:
If you organize Accounts and Items (as well as several other very useful) QuickBooks lists in an outline format, you will have a great deal of control over what you see as you monitor your reports. For example, whenever you create a ‘header’ Item, Account, Customer, Class, or Customer Type, QuickBooks will automatically create a subtotal in the resulting report.
After you’ve carefully designed the structure of your lists, you can begin to implement the pM3 approach to achieving your gross profit goals.
Step 1: PLAN
5 Ways to Use QuickBooks to Establish & Clarify Your PLANS
Are Your Plans and Targets “Fuzzy” (or Maybe Even Missing-In-Action)?
Companies that don’t create specific financial plans lose out on three key elements of the control system (planning, monitoring, and managing by exception) and that’s a big price to pay. It’s likely that they’ll see the negative impact in both their gross and net profits.
Enter Your Plans and Standards into QuickBooks
-
Establish and Enter Your Big Picture (Gross and Net Profit) Plan Into QuickBooks
 Start with your desired bottom line (net profit) goal for the company, then add back the following amounts (by account):
Start with your desired bottom line (net profit) goal for the company, then add back the following amounts (by account):
-
- Reasonable compensation for the owner BEFORE seeing bottom-line profits
- All other company overhead
- General (non-job-specific) construction/production costs
The result reveals your gross profit goal. Because gross profit consists of Gross Sales minus “Cost of Goods Sold (COGS),” you’ll need to convert your goal into these two elements (income and costs required to produce the income).
Review your results; if they don’t appear to be achievable, revise each of your numbers until you believe they are achievable.
To enter your company’s gross profit, gross sales, and cost of goods sold goals into QuickBooks, simply go to:
-
- Company > Planning & Budgeting > Set up Budgets
- Choose the year, “No additional criteria,” and “Create budget from scratch”
You’ll then be able to enter your planned income and expenditures by account, by month.
-
Create Job Estimates That Line Up With Your Gross Profit Target
After you’ve developed your Item List, use the QuickBooks Estimates feature to record your estimated job costs and income by job stage. You can choose from a variety of methods, including:
-
- “Double” Estimates: One ‘cost only’ Estimate (for Internal Use) plus one ‘income only’ Estimate (to provide to your customer)
- “Single” Estimate for both cost and income (variety of options available)
-
Don’t Let Change Orders Slip Through the Cracks When It Comes to Gross Profits
When you create Change Orders, be sure that each of them will meet or exceed your gross profit target. Nothing can erode your Gross Profit results faster than below-target (or unrecorded) Change Orders!
-
Meet Your Estimated Gross Profit Goals By Using Purchase Orders to Nail Down Costs
There are many planning and control reasons to use PO’s – including:
-
- Clarifying your needs before contacting the vendor
- Outlining quality and timing expectations
- Running QuickBooks “Open Purchase Orders by Job” reports
- Fast, accurate conversion – from the PO into a QuickBooks Bill
- Cost review and control before Bills are approved and paid
- QuickBooks makes it extremely easy to create Purchase Orders directly from Estimates (just point and click) without having to re-enter data.
-
Use the QuickBooks ‘Memorized Transactions’ Feature
If you have similar, recurring transactions, be sure to investigate how you can memorize and then re-use (and modify) Estimates, Purchase Orders, and other transactions. You can even set up and enter groups of memorized transactions. It just doesn’t get much easier.
Step 2: Measure
Use Quickbooks to Measure Job Costing Income & Company Gross Profit
Enter job costs and income using these QuickBooks transactions
As your jobs progress, enter job costs using Bills, Checks, and Credit Cards. At the bottom of the data entry screen for each of these types of transactions, you’ll see two tabs:
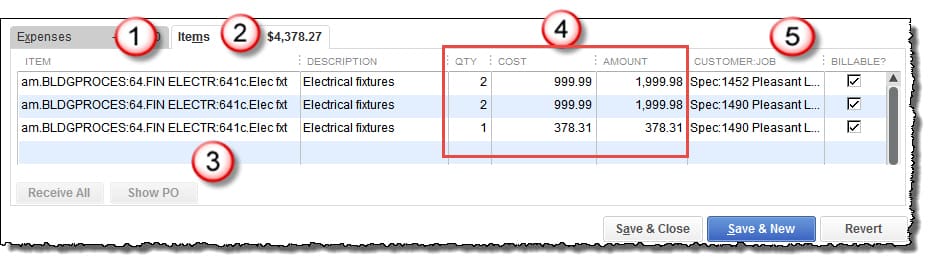
- Tab #1 is the tab you will choose to enter an account (use these primarily for non-job entries).
- Use Tab #2 and the Items (#3) that you created to enter Quantity, Unit cost, and Total $ Amount (#4).
- After you’ve selected the correct Item, assign every job cost to a job (#5).
If you have job-related costs that you cannot reasonably assign to a specific job, create a job called “NJS – (Non-Job-Specific).” This will help to ensure that EVERY job-related cost is assigned somewhere. This helps greatly with month-end proofing and balancing.
Enter Income using Invoices or Sales Receipt transactions. This will ensure that you’ll see income in the correct column on detailed job cost reports.
QuickBooks Data-Entry Hint:
Nearly all data should be entered using these types of QuickBooks transactions. Journal entries are appropriate only for very specific circumstances.
Step 3: Monitor
Use QuickBooks Reports To Compare Planned To Actual Results
Here are just some of the reports you can use to monitor and track your targeted company and job gross profit results:
-
QuickBooks Budget vs. Actual Profit & Loss
(This month and year-to-date). Check your company-wide Gross Profit amounts and percentages.
-
QuickBooks Profit & Loss by Job
(Account-based) reports. Check Gross Profit amounts and percentages for individual jobs.
-
QuickBooks Job Profitability and/or Estimate vs. Actual
(Item-based) reports. Check Item details to see if actuals appear reasonable.
-
QuickBooks Open Purchase Orders by Job Report.
Check these reports to see what costs are ‘committed’ but not yet entered into job costing reports.
Step 4: Modify or Take Corrective Action
Apply YOUR Knowledge and Expertise…
 You can manage by exception by following up on current activities that are out of alignment, finding out why, and seeing what can be done. You may be able to make immediate changes, or you may discover how to improve future operations. But before taking any drastic steps, it’s a best practice to be sure that you’ve completed month-end proofing, balancing, and closing procedures and verified that your data reflects reality.
You can manage by exception by following up on current activities that are out of alignment, finding out why, and seeing what can be done. You may be able to make immediate changes, or you may discover how to improve future operations. But before taking any drastic steps, it’s a best practice to be sure that you’ve completed month-end proofing, balancing, and closing procedures and verified that your data reflects reality.
Alternatively, you may discover a problem in an assumption or calculation used in the budget or an estimate. That provides information you can use to fix the issue by revising the standard.
Deciding when, where, and how to implement these modifications and corrections is, of course, a function of company management.
Is It Worthwhile to Follow the “pM3 Business Management Model”?
The goal of the pM3 process is a continual, managed improvement – and a major segment of financial improvement is to achieve gross profit targets. Each time you repeat the pM3 cycle, you’ll find that you can get closer and closer to your established goals.
If you take advantage of the tools and management reporting controls that QuickBooks provides to record Plans, Measure data, and Monitor results, you’ll be able to more easily Modify, focus on, and achieve the goals you’ve established.
The tools are at hand!
People Also Ask
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is job costing in QuickBooks?
Job costing in QuickBooks allows businesses to track expenses and revenue for specific jobs or projects. You then use that information to achieve insights into profitability and cost efficiency.
2. How do I set up job costing in QuickBooks?
To set up job costing in QuickBooks, assign a job or project to each transaction (including payroll), and use Items (or even Accounts) to accurately assign costs.
3. What are the benefits of using job costing in QuickBooks?
Job costing helps businesses accurately assign costs to jobs, analyze profitability on a per-job basis, make informed pricing decisions based on increased knowledge, and use the job costing information to improve overall financial management.
4. What is gross profit, and why is it important for businesses using QuickBooks?
Gross profit is revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). It indicates how efficiently a business produces goods or services before deducting operating expenses. Monitoring gross profit helps businesses assess profitability and set financial goals.
5. How can I calculate gross profit in QuickBooks?
QuickBooks uses accounts assigned to account types to automatically calculate gross profit using the formula Sales – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). To ensure accurate reporting, review your income and COGS accounts. Check to see that your accounts are properly assigned to the correct TYPE of account (Income of COGS) and that your sales and cost transactions are linked to (appearing in) the correct accounts.
6. What are typical gross profit goals for businesses using QuickBooks?
Gross profit goals vary by industry and business size but generally aim to cover overhead costs plus generate a healthy profit margin. Setting realistic goals helps businesses track performance and make strategic decisions.
7. How can I improve gross profit margins in QuickBooks?
To improve gross profit margins, businesses can negotiate better supplier deals, streamline operations to reduce costs, optimize pricing strategies, and focus on higher-margin products or services.
8. What are some common challenges businesses face when managing job costs in QuickBooks?
Challenges include inaccurate cost assignments, failing to track all job-related expenses, not comparing job costs with revenue on a timely (or percentage of completion) basis, and overlooking indirect costs that affect project profitability.
9. Can QuickBooks generate reports to track job costs and gross profit?
Yes, QuickBooks offers customizable reports like Job Profitability, Estimate vs. Actual Job Costing Reports, and account-based Profit & Loss by Job reports. Each type of report provides various detailed insights into job costs, revenue, and gross profit and assists with making informed decisions.
10. Where can I find more resources and guides on using QuickBooks for job costing and setting gross profit goals?
Additional resources and guides are available on the Build Your Numbers website.
![]()
Learn more about Job Costing:
5 Ways to Use Job Costing to Increase Your Gross Profits
5 Reasons Construction Businesses Need Job Costing
The Many Faces of Construction Job Costing
…
An earlier version of this article first appeared in the Builder Partnerships newsletter.
Customer Praise For Diane Gilson, Info Plus Consulting, and BuildYourNumbers.com
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ From the Intuit FindAProAdvisor website:
“Diane has been our go-to Quickbooks consultant for years. We consider her the top expert in the nation for the home building industry.”
See More Customer and Client Comments

